rfid radio frequency identification chips used to track packages cost Logistics and supply chain management are increasingly turning to radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to provide real-time visibility into the locations and quantities of materials and items. The use of RFID tags can speed the inventory management process, reduce opportunities for human error and help reduce inventory shrinkage. WTGZ Tiger 95.9 player. WTGZ Tiger 95.9. Your station will play momentarily. .
0 · what is rfid technology
1 · rfid tags for logistics
2 · rfid supply chain management
3 · rfid scanning technology
4 · rfid logistics tracking
5 · radio frequency identification
6 · logistics rfid technology
My recommendation is to search the web for access to the best hand available based on cards in your hand and cards on the table. You then link the NFC tag to your URL that allows you to .
Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID, high-frequency RFID offers the following advantages: .
Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID, high-frequency RFID offers the following advantages: Shorter Reading Distance: Typically between 1 and 2 meters, making it more effective .
Logistics and supply chain management are increasingly turning to radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to provide real-time visibility into the locations and quantities of materials and items. The use of RFID tags can speed the inventory management process, reduce opportunities for human error and help reduce inventory shrinkage.
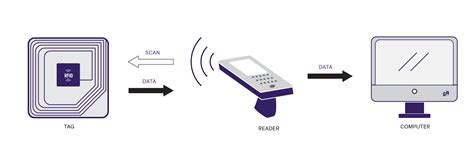
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology used to identify and track objects wirelessly using radio waves. Essentially, it allows for the automatic identification and data capture of items, providing valuable insights into their location and status. RFID, or radio-frequency identification, refers to technology that captures data encoded in labels and tags with a reader via radio waves. RFID technology is similar to a barcode or the magnetic stripe of a credit card, as the data encoded in the label or magnetic strip can be captured by a device and stored in a database.What is EPC Memory? EPC (Electronic Product Code) memory is a specific type of memory found in RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chips. It is used to store the unique identification number of an item or product.RFID is a wireless technology that uses radio frequency fields to transfer data. It is the same technology commonly used in pet microchipping and passports. RFID gives a person the ability to track and identify inventory in real time. With this kind of control, warehouse management can always know where inventory is located within the supply chain.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) asset tracking uses a system of RFID tags and electromagnetic readers to collect data from fixed assets or movable assets. RFID tracking involves. 1. Improved Inventory Management and Accuracy. An RFID system enables real-time inventory tracking, so companies can quickly and accurately locate items in their warehouses or throughout the supply chain journey. This decreases the risk of stockouts, overstocking, and the associated costs.
RFID tagging involves small devices that use radio frequencies to transfer data, mainly to track and identify objects, animals and people. Learn more here. open access. Highlights. •. Presents a critical perspective of the recent advancement of the RFID humidity, temperature, gas, pH, integrity, and traceability sensor for food packaging. •. Explains the existing challenges of RFID sensor technology.Advantages of High-Frequency (HF) Chips. The NXP ICODE® chip series operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which falls within the high-frequency (HF) RFID range. Compared to ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID, high-frequency RFID offers the following advantages: Shorter Reading Distance: Typically between 1 and 2 meters, making it more effective .
Logistics and supply chain management are increasingly turning to radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to provide real-time visibility into the locations and quantities of materials and items. The use of RFID tags can speed the inventory management process, reduce opportunities for human error and help reduce inventory shrinkage. RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology used to identify and track objects wirelessly using radio waves. Essentially, it allows for the automatic identification and data capture of items, providing valuable insights into their location and status. RFID, or radio-frequency identification, refers to technology that captures data encoded in labels and tags with a reader via radio waves. RFID technology is similar to a barcode or the magnetic stripe of a credit card, as the data encoded in the label or magnetic strip can be captured by a device and stored in a database.What is EPC Memory? EPC (Electronic Product Code) memory is a specific type of memory found in RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chips. It is used to store the unique identification number of an item or product.
how much does an rfid reader costs
RFID is a wireless technology that uses radio frequency fields to transfer data. It is the same technology commonly used in pet microchipping and passports. RFID gives a person the ability to track and identify inventory in real time. With this kind of control, warehouse management can always know where inventory is located within the supply chain. Radio-frequency identification (RFID) asset tracking uses a system of RFID tags and electromagnetic readers to collect data from fixed assets or movable assets. RFID tracking involves.
1. Improved Inventory Management and Accuracy. An RFID system enables real-time inventory tracking, so companies can quickly and accurately locate items in their warehouses or throughout the supply chain journey. This decreases the risk of stockouts, overstocking, and the associated costs.
RFID tagging involves small devices that use radio frequencies to transfer data, mainly to track and identify objects, animals and people. Learn more here.
how do passive rfid tags get power
what is rfid technology
rfid tags for logistics
how much data is an rfid card able to store
The Thales Gemalto smartcards that we keep in stock include the popular IDPrime minidriver .
rfid radio frequency identification chips used to track packages cost|radio frequency identification