implantable combination rfid gps implant tracking chip Researchers at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, led by Professor Dina Katabi, have developed ReMix, an "in-body GPS system" that utilizes wireless technology to. Relay: Relays NFC traffic between two devices using a server. One device operates as a .Smart Card Emulator. Use your phone as contact-less smart card. The Android Smart Card Emulator allows the emulation of a contact-less smart. card. The emulator uses Android's HCE to fetch process APDUs from a NFC .
0 · rfid microchip implant
1 · remix implant tracking
2 · injectable chip tracking
3 · implantable chip tracking
4 · implantable chip health tracker
5 · how to get rfid implanted
6 · gps implants for body
7 · gps implant tracking system
The US was the market that literally set the standards and led the world on card payments. Another, was the belief that mobile payments would replace the need for plastic altogether and NFC cards .
Researchers at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, led by Professor Dina Katabi, have developed ReMix, an "in-body GPS system" that utilizes wireless technology to.Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body. Researchers at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, led by Professor Dina Katabi, have developed ReMix, an "in-body GPS system" that utilizes wireless technology to.Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body.
The new method can pinpoint the location of ingestible implants inside the body using low-power wireless signals. These implants could be used as tiny tracking devices on shifting tumors to help monitor their slight movements.
Working with the world’s leading chip fabrication giant, they’ve created an ultrasound-powered, injectable, fully functioning single-chip system that’s so tiny it could one day enter the human. Chips sold for implants are generally either low or high frequency. RFID chips are identified using radio waves, and near-field communication (NFC) chips are a branch of high-frequency.
Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms, a.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
rfid microchip implant
In 2004, Florida-based Applied Digital Solutions received FDA approval to market the use of Verichips: an ID chip implanted under the skin that would be used for medical purposes. The chip would contain a 16-digit number that could be scanned by . A human microchip implant is a device inserted beneath your skin. It’s made of biocompatible silicate glass and is similar in size to a grain of rice. These microchip implants leverage radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to store and transmit data. Other payment implants are based on radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is the similar technology typically found in physical contactless debit and credit cards.
Researchers at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, led by Professor Dina Katabi, have developed ReMix, an "in-body GPS system" that utilizes wireless technology to.
Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body.
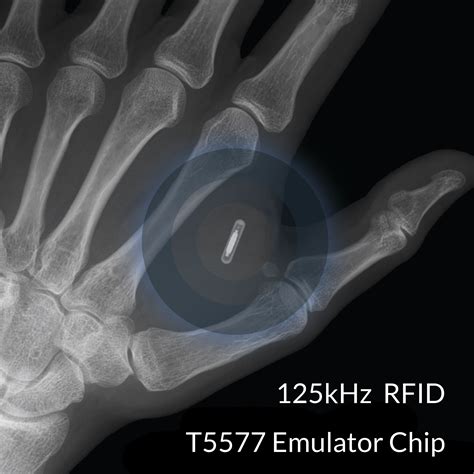
The new method can pinpoint the location of ingestible implants inside the body using low-power wireless signals. These implants could be used as tiny tracking devices on shifting tumors to help monitor their slight movements. Working with the world’s leading chip fabrication giant, they’ve created an ultrasound-powered, injectable, fully functioning single-chip system that’s so tiny it could one day enter the human. Chips sold for implants are generally either low or high frequency. RFID chips are identified using radio waves, and near-field communication (NFC) chips are a branch of high-frequency. Sure, the technology—a millimeters-long microchip equipped with near-field communication capabilities and lodged just under the skin—had a niche, cutting-edge appeal, but in practical terms, a.
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.In 2004, Florida-based Applied Digital Solutions received FDA approval to market the use of Verichips: an ID chip implanted under the skin that would be used for medical purposes. The chip would contain a 16-digit number that could be scanned by . A human microchip implant is a device inserted beneath your skin. It’s made of biocompatible silicate glass and is similar in size to a grain of rice. These microchip implants leverage radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to store and transmit data.
high antenna rf readings

mifare 1k card suppliers
Part 1 of the standard specifies that the card shall be compliant with ISO/IEC 7810 or ISO/IEC 15457-1, or "an object of any other dimension". See more
implantable combination rfid gps implant tracking chip|injectable chip tracking