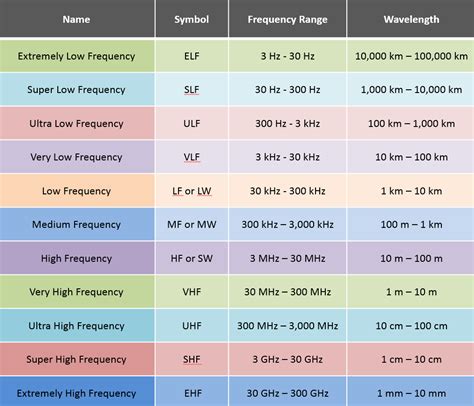
difference between high frequency and low frequency rfid tags The ultra high frequency range includes frequencies from 300 to 1000 MHz, but only two frequency ranges, 433 MHz and 860–960 MHz, are used for RFID applications. The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags, while the 860–960 MHz range is used mostly for passive tags and some semi-passive tags.
Nov 11, 2024. In today’s rapidly evolving financial technology landscape, .
0 · rfid frequency chart
1 · rf frequency range chart
2 · low frequency rfid range
3 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
4 · difference between rfid labels
5 · 13 56 mhz rfid tag
6 · 125khz rfid tags
7 · 125khz rfid tag sticker
Award. Share. Epikgamer332. • 1 yr. ago. NFC isn't located in the joystick, rather, in front of the joystick box only on the right side joycon. Hopefully you can make out the black piece that .
What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency RFID? Low Frequency (LF) RFID works between 125 kHz and 134 kHz. High Frequency (HF) RFID is at . Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware. What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency RFID? Low Frequency (LF) RFID works between 125 kHz and 134 kHz. High Frequency (HF) RFID is at 13.56 MHz. LF RFID reads shorter distances and slower than HF RFID. But, it works better with water and metal. HF RFID, like NFC, is global and works with smartphones. What are RFID tags? Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.
High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a wide range of storing capacities and read distances ranging from millimeters to meters.The ultra high frequency range includes frequencies from 300 to 1000 MHz, but only two frequency ranges, 433 MHz and 860–960 MHz, are used for RFID applications. The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags, while the 860–960 MHz range is used mostly for passive tags and some semi-passive tags.
What is the difference between high- and low-frequency RFID? LF works at short distances, ideal for environments with metal/liquids. HF offers longer range and handles more data, suitable for access control.
This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency). Home. FAQ. LF, HF, and UHF Frequency: What’s the Difference? RFID technology uses radio waves to transmit data between an RFID tag and the reader. The frequency of the tag determines its read distance and affects its functionality.This means that a low frequency RFID wave, which operates at 125 KHz, produces 125,000 waves per second. An ultra-high frequency RFID wave, on the other hand, produces 3,000,000,000 waves per second since UHF operates up to 3 GHz.Although HF tags have a lower transmission rate compared to UHF tags, they can store more data and are equipped with anti-collision features, allowing multiple tags to be read simultaneously. Design and cost advantage. Manufacturers usually make HF tag antennas from copper, silver, or aluminum coils, which are simple in design and low in cost.
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware. What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency RFID? Low Frequency (LF) RFID works between 125 kHz and 134 kHz. High Frequency (HF) RFID is at 13.56 MHz. LF RFID reads shorter distances and slower than HF RFID. But, it works better with water and metal. HF RFID, like NFC, is global and works with smartphones. What are RFID tags? Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags. High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a wide range of storing capacities and read distances ranging from millimeters to meters.
The ultra high frequency range includes frequencies from 300 to 1000 MHz, but only two frequency ranges, 433 MHz and 860–960 MHz, are used for RFID applications. The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags, while the 860–960 MHz range is used mostly for passive tags and some semi-passive tags.
What is the difference between high- and low-frequency RFID? LF works at short distances, ideal for environments with metal/liquids. HF offers longer range and handles more data, suitable for access control.This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency). Home. FAQ. LF, HF, and UHF Frequency: What’s the Difference? RFID technology uses radio waves to transmit data between an RFID tag and the reader. The frequency of the tag determines its read distance and affects its functionality.This means that a low frequency RFID wave, which operates at 125 KHz, produces 125,000 waves per second. An ultra-high frequency RFID wave, on the other hand, produces 3,000,000,000 waves per second since UHF operates up to 3 GHz.
smart card new carrd or old card enrollment

rfid frequency chart
rf frequency range chart
This video focuses on a PN532 NXP NFC/RFID Module , its working , .NFC is no exception here, with libnfc having been around for a quite some time—in fact, it's the original reason the NFC Breakout was developed! libnfc is a library for C programmers. For Python and .
difference between high frequency and low frequency rfid tags|difference between rfid labels