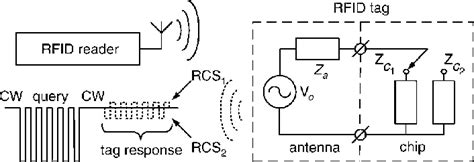
rfid tag internal circuit In this paper, we analyze one of the most common UHF RFID tag antenna structures, a T-matched dipole. We for the first time derive the closed-form solutions for the resonant frequencies of tag sensitivity and backscatter responses as functions of tag equivalent circuit parameters.
Try the Tag Reader in Control Center. If your iPhone isn’t automatically recognizing NFC tags, you can try using the NFC Tag Reader tool that’s built into your iPhone. However, this is only .
0 · Tag Tuning/RFID Application Note
1 · RFID Tag Analysis Using an Equivalent Circuit
2 · RFID Reader and Tag
3 · Passive RFID Basics
4 · How Are RFID Tags Powered
5 · Active vs. Passive RFID Tags: Unveilin
KGRG 89.9 FM (KGRG-FM 89.9 FM) is an Alternative radio station licensed to Auburn, WA, and serves the Seattle-Tacoma radio market. The station is currently owned by Green River College. Call sign: KGRG-FM Frequency: .Statewide coverage is the hallmark of the Auburn Sports Network's exclusive coverage of Auburn football. All home and away games are broadcast across the entire state of Alabama plus portions of .
Typical RFID tag with a T-matched antenna. Tag performance can be characterized by tag sensitivity (also called threshold POTF, Power on Tag Forward) and tag backscatter (also called POTR, Power on Tag Reverse). A typical response of a T-matched tag is shown in Fig. 2 .The efficient transfer of energy from the reader to the tag directly affects operational reliability .Typical RFID tag with a T-matched antenna. Tag performance can be characterized by tag sensitivity (also called threshold POTF, Power on Tag Forward) and tag backscatter (also called POTR, Power on Tag Reverse). A typical response of a T-matched tag is shown in Fig. 2 where both POTF and POTR are at tag threshold.The efficient transfer of energy from the reader to the tag directly affects operational reliability and read/write range. Generally, both 13.56 MHz and 125 kHz RFID tags use parallel resonant LC loop antennas, tuned to the carrier frequency. This application note gives an overview of basic tag antenna tuning.
Active RFID tags are powered by their internal battery, which sets them apart from passive RFID tags. The battery supplies the required energy to the microchip and antenna of the active tag, enabling it to operate independently and transmit signals over longer distances.
In this paper, we analyze one of the most common UHF RFID tag antenna structures, a T-matched dipole. We for the first time derive the closed-form solutions for the resonant frequencies of tag sensitivity and backscatter responses as functions of tag equivalent circuit parameters.RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data stored on) an RFID tag. Tags are embedded in small items like cards, buttons, or tiny capsules. These readers also use radio waves in some systems to write new information to the tags.
A passive RFID tag contains an RFID integrated circuit (IC), resonant capacitor (C), and antenna (L), as shown in Figure 1. The antenna and capacitor form a parallel LC resonant circuit. The LC circuit must be tuned to the reader’s carrier frequency for maximum performance (read range).This circuit integrates an Arduino UNO microcontroller with an RFID-RC522 module, a 16x2 LCD screen with an I2C interface, and a servo motor. The Arduino UNO serves as the central processing unit, controlling the RFID reader for tag scanning, displaying information on the LCD, and driving the servo motor based on the program logic.
Tag Tuning/RFID Application Note
Learn the different components that go into an RFID Tag such as RFID chip, inlay, antenna and strap. Choosing the best RFID is important for any RFID project. RFID tags are used in many industries and you can find them in product tags from stores to security access cards. RFID tags can expedite the checkout and can be used for antitheft measures. They can be also used for identifying livestock, products, etc. In this tutorial, we will learn how we can use the RFID technology with the Arduino.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems use radio frequency to identify, locate and track people, assets, and animals. Passive RFID systems are composed of three components – an interrogator (reader), a passive tag, and a host computer. The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry .
Typical RFID tag with a T-matched antenna. Tag performance can be characterized by tag sensitivity (also called threshold POTF, Power on Tag Forward) and tag backscatter (also called POTR, Power on Tag Reverse). A typical response of a T-matched tag is shown in Fig. 2 where both POTF and POTR are at tag threshold.
The efficient transfer of energy from the reader to the tag directly affects operational reliability and read/write range. Generally, both 13.56 MHz and 125 kHz RFID tags use parallel resonant LC loop antennas, tuned to the carrier frequency. This application note gives an overview of basic tag antenna tuning.

Active RFID tags are powered by their internal battery, which sets them apart from passive RFID tags. The battery supplies the required energy to the microchip and antenna of the active tag, enabling it to operate independently and transmit signals over longer distances.In this paper, we analyze one of the most common UHF RFID tag antenna structures, a T-matched dipole. We for the first time derive the closed-form solutions for the resonant frequencies of tag sensitivity and backscatter responses as functions of tag equivalent circuit parameters.RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data stored on) an RFID tag. Tags are embedded in small items like cards, buttons, or tiny capsules. These readers also use radio waves in some systems to write new information to the tags.A passive RFID tag contains an RFID integrated circuit (IC), resonant capacitor (C), and antenna (L), as shown in Figure 1. The antenna and capacitor form a parallel LC resonant circuit. The LC circuit must be tuned to the reader’s carrier frequency for maximum performance (read range).
This circuit integrates an Arduino UNO microcontroller with an RFID-RC522 module, a 16x2 LCD screen with an I2C interface, and a servo motor. The Arduino UNO serves as the central processing unit, controlling the RFID reader for tag scanning, displaying information on the LCD, and driving the servo motor based on the program logic.Learn the different components that go into an RFID Tag such as RFID chip, inlay, antenna and strap. Choosing the best RFID is important for any RFID project. RFID tags are used in many industries and you can find them in product tags from stores to security access cards. RFID tags can expedite the checkout and can be used for antitheft measures. They can be also used for identifying livestock, products, etc. In this tutorial, we will learn how we can use the RFID technology with the Arduino.
smart ration card form download in tamil nadu
smart phone card international
AUBURN — The 2023 Auburn football season will introduce several new affiliates, as well as the addition of two familiar faces in new roles with the Auburn Sports Network .
rfid tag internal circuit|Passive RFID Basics