stanford engineer rf id Silicon technology modeling both for digital and analog circuits, including . Description of NFC Tools. NFC Tools is an app which allows you to read, write and program tasks on your NFC tags and other compatible NFC chips. Simple and intuitive, NFC .
0 · Wireless sensors stick to the skin like band
1 · Wireless sensors stick to skin and track health
2 · Warren Hausman
3 · Thomas Lee's Profile
4 · Thomas Lee
5 · SMIrC Lab
6 · Integrated Circuits and Systems
Manage your Citi credit card account online, pay bills, view statements, and access exclusive .
Now, Stanford engineers have developed a way to detect physiological signals emanating from the skin with sensors that stick like band-aids and beam wireless readings to a .Professor Lee's principal areas of professional interest include analog .Silicon technology modeling both for digital and analog circuits, including .Professor of Electrical Engineering. Professor Lee's principal areas of .
To get around this problem, the Stanford researchers developed a new type of RFID system that could beam strong and accurate signals to the receiver despite constant fluctuations. The battery-powered receiver then uses .Professor Lee's principal areas of professional interest include analog circuitry of all types, ranging from low-level DC instrumentation to high-speed RF communications systems. His present .
Warren Hausman. Professor Hausman performs research in operations planning and control, with specific interests in supply chain management. Most of his contributions are based upon .Silicon technology modeling both for digital and analog circuits, including optoelectronic/RF applications, bio-sensors and computer-aided bio-sensor design, wireless implantable sensors.Through the years, the SMIrC laboratory has been a driving force in developing the theory of radio frequency (RF) CMOS integrated circuit design as well as in educating tomorrow's RFIC .
Professor of Electrical Engineering. Professor Lee's principal areas of professional interest include analog circuitry of all types, ranging from low-level DC instrumentation to high-speed RF . Now, Stanford engineers have developed a way to detect physiological signals emanating from the skin with sensors that stick like band-aids and beam wireless readings to a receiver clipped onto clothing.
To get around this problem, the Stanford researchers developed a new type of RFID system that could beam strong and accurate signals to the receiver despite constant fluctuations. The battery-powered receiver then uses Bluetooth to periodically upload data from the stickers to a smartphone, computer or other permanent storage system.Professor Lee's principal areas of professional interest include analog circuitry of all types, ranging from low-level DC instrumentation to high-speed RF communications systems. His present research focus is on CMOS RF integrated circuit design, and on extending operation into the terahertz realm.Warren Hausman. Professor Hausman performs research in operations planning and control, with specific interests in supply chain management. Most of his contributions are based upon quantitative modeling techniques and emphasize relevance and real world applicability. He has recently studied how RFID technology can revolutionize the management .
Silicon technology modeling both for digital and analog circuits, including optoelectronic/RF applications, bio-sensors and computer-aided bio-sensor design, wireless implantable sensors.Through the years, the SMIrC laboratory has been a driving force in developing the theory of radio frequency (RF) CMOS integrated circuit design as well as in educating tomorrow's RFIC designers.Professor of Electrical Engineering. Professor Lee's principal areas of professional interest include analog circuitry of all types, ranging from low-level DC instrumentation to high-speed RF communications systems.
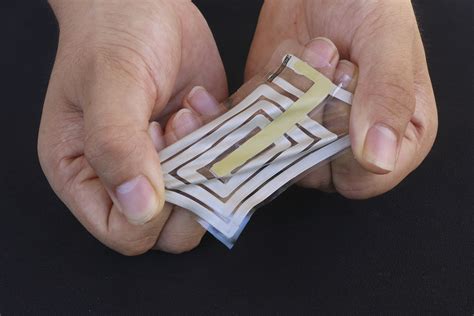
H.-S. Philip Wong - Willard R. and Inez Kerr Bell Professor in the School of Engineering and Professor of Electrical Engineering. Dr. Wong's present research covers a broad range of topics including carbon electronics, 2D layered materials, wireless implantable biosensors, directed self-assembly, nanoelectromechanical relays, device modeling . The BodyNet sticker is similar to the ID card: It has an antenna that harvests a bit of the incoming RFID energy from a receiver on the clothing to power its sensors. It then takes readings from the skin and beams them back to the nearby receiver.Stanford University Catalog . Academic Calendar 2022-23 Schedule of Classes Bulletin Archive Get Help Academic Calendar 2022-23 . Course Description. Design, testing, and applications of Radio Frequency (RF) electronics: Amplitude Modulation (AM), Frequency Modulation (FM) and concepts of Software Define Radio (SDR) systems. Practical aspects . Now, Stanford engineers have developed a way to detect physiological signals emanating from the skin with sensors that stick like band-aids and beam wireless readings to a receiver clipped onto clothing.
To get around this problem, the Stanford researchers developed a new type of RFID system that could beam strong and accurate signals to the receiver despite constant fluctuations. The battery-powered receiver then uses Bluetooth to periodically upload data from the stickers to a smartphone, computer or other permanent storage system.
Professor Lee's principal areas of professional interest include analog circuitry of all types, ranging from low-level DC instrumentation to high-speed RF communications systems. His present research focus is on CMOS RF integrated circuit design, and on extending operation into the terahertz realm.Warren Hausman. Professor Hausman performs research in operations planning and control, with specific interests in supply chain management. Most of his contributions are based upon quantitative modeling techniques and emphasize relevance and real world applicability. He has recently studied how RFID technology can revolutionize the management .
Silicon technology modeling both for digital and analog circuits, including optoelectronic/RF applications, bio-sensors and computer-aided bio-sensor design, wireless implantable sensors.Through the years, the SMIrC laboratory has been a driving force in developing the theory of radio frequency (RF) CMOS integrated circuit design as well as in educating tomorrow's RFIC designers.Professor of Electrical Engineering. Professor Lee's principal areas of professional interest include analog circuitry of all types, ranging from low-level DC instrumentation to high-speed RF communications systems.
Wireless sensors stick to the skin like band
H.-S. Philip Wong - Willard R. and Inez Kerr Bell Professor in the School of Engineering and Professor of Electrical Engineering. Dr. Wong's present research covers a broad range of topics including carbon electronics, 2D layered materials, wireless implantable biosensors, directed self-assembly, nanoelectromechanical relays, device modeling . The BodyNet sticker is similar to the ID card: It has an antenna that harvests a bit of the incoming RFID energy from a receiver on the clothing to power its sensors. It then takes readings from the skin and beams them back to the nearby receiver.
sigmakey smart card service is stopped
shell hellas smart club card
Contactless cards use Near Field Communication (NFC) to enable transactions, a subset of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). Compared to RFID, NFC works for smaller distances in the range of ten centimeters, while .Fourteen teams will make the NFL playoffs — seven from both the NFC and AFC. This is an increase over the previous format, which had 12 teams. This is broken out with four division winners in each conference as well as three wild-card teams. See more
stanford engineer rf id|Thomas Lee